The Basics of Water Purification Explained
PUBLISHED ON: 25-Sept-2025
Only about three percent of Earth’s water is fresh, and from that, barely 1.2 percent is accessible as drinking water, according to National Geographic. The rest lies frozen in glaciers, sealed in ice caps, or hidden deep beneath the ground. The fraction that sustains us flows through rivers and streams, sources that have shaped human civilisation and continue to be the lifeline of ecosystems worldwide.
Clean and safe water is something we often take for granted, yet the water reaching our taps is rarely free from contaminants. Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and ageing pipelines often taint it with chemicals, microbes, and dissolved salts. That is where the purification of water becomes essential. Modern water purification methods such as RO, UV, and UF are no longer luxuries; they are safeguards, ensuring that every drop is not only safe but also enriched, sometimes with essential minerals like copper, to support healthier living.
Understanding Water Purification Methods
Water purification is the process of removing contaminants, ranging from dissolved salts and heavy metals to microorganisms and sediments, from water. Over time, various methods have been developed to tackle different impurities:
- Boiling – An age-old practice that kills bacteria and viruses but cannot remove chemicals, salts, or heavy metals.
- Chlorination – Widely used in municipal supply systems, effective against microbes but leaves behind a chemical taste and sometimes harmful by-products.
- Distillation – Produces clean water but is impractical for households due to cost and energy use.
- Filtration with activated carbon – Removes chlorine, odours, and some organic impurities, but is limited against dissolved salts or pathogens.
While these methods have their uses, modern water challenges, especially in cities, require more advanced technologies. This is where RO, UV, and UF purification systems step in.
- Modern Purifiers (RO, UV, UF) – Advanced technologies that remove a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, microbes, and sediments, ensuring safe and healthy water for daily use.
RO, UV, and UF: The Core of Water Purification
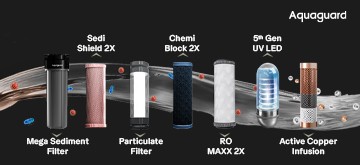
Reverse Osmosis (RO)
RO, or reverse osmosis, uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved salts, fluoride, arsenic, nitrates, and heavy metals. It is particularly effective in areas with hard water or high TDS (total dissolved solids). An RO water filter ensures clean water that is safe for long-term consumption.
Ultraviolet (UV) Purification
UV purification uses UV light to deactivate bacteria, viruses, and pathogens. While it doesn’t remove salts or chemicals, it ensures the microbial safety of water. When paired with RO, it forms a powerful combination against both physical and biological contaminants.
Ultrafiltration (UF)
UF is a membrane-based method that removes larger particles, sediments, and some microorganisms. It works without electricity, making it an energy-efficient support system for RO and UV.
Together, RO, UV, and UF water purification methods cover most potential contamination types, making them a reliable trio for household water purification.
A major challenge many households face is the frequent replacement of purifier filters, which can be both time-consuming and costly. Short filter life often interrupts daily use, making it harder to consistently enjoy clean, safe water.
Why Filter Life Matters in Purification
While technology often gets the spotlight, another factor making a difference is filter life. Typically, water purifiers require frequent cartridge changes, adding to the cost and hassle of ownership. But advanced purifiers today come with a 2-year filter life, ensuring longer-lasting performance and fewer interruptions. This not only makes maintenance more manageable but also reflects how innovations are prioritising both efficiency and user convenience.
Bringing It All Together
The purification of water is no longer about a single method or a temporary fix; it’s about combining the right technologies to deal with multiple contaminants at once. Traditional methods like boiling or chlorination might still work for emergencies, but in urban and semi-urban settings where water quality is unpredictable, RO, UV, and UF purification methods have emerged as the gold standard.
Modern purifiers like the Aquaguard Ritz Pro 2X Life and Aquaguard Blaze Insta WS show how innovation is addressing not only contamination but also practical concerns like filter life, smart monitoring, and convenience features.
In essence, water purification is evolving from being a basic need to a smart, sustainable, and user-friendly process. And with water quality continuing to be a pressing issue worldwide, understanding these basics ensures that every glass of water at home is safe and pure.
Why is it important to use advanced water purification methods even if the water looks clean?
Even clear-looking water can contain invisible contaminants such as dissolved salts, bacteria, viruses, pesticides, and heavy metals. Advanced methods like RO, UV, and UF ensure these hidden impurities are removed, making the water truly safe to drink.
How does a copper-enriched water purifier benefit health?
Copper is known for its natural antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. A purifier that infuses copper into water can help improve immunity, support digestion, and contribute to overall well-being, making every glass of water healthier.
What makes long filter life important in water purifiers?
A purifier with a long filter life, such as 2 years, reduces the hassle and cost of frequent replacements. It ensures consistent purification performance, giving families uninterrupted access to safe, clean water without worrying about sudden filter exhaustion.
